Reflecting on the history of Blockchain reveals that the technology’s rise to prominence was largely due to its affiliation with Bitcoin, a revolutionary digital asset.
In the past, the terms Bitcoin and Blockchain were often interchanged and conflated by many individuals globally. However, with increased understanding and clarity about the technology, the gap between Blockchain and Cryptocurrency has widened, leading to the emergence of numerous powerful applications for Blockchain beyond the realm of digital currency.
Now, Blockchain’s non-cryptocurrency applications have not only highlighted that Bitcoin is merely one component of the technology but have also underscored its potential to solve two universal business problems – security and transparency.
This article will delve into some of the key applications of blockchain across diverse industries and highlight brands that are shifting the narrative from ‘what is blockchain technology’ to ‘what are the practical applications of blockchain technology in business and life’.
Let’s take a brief journey through time to trace how the applications of blockchain technology have evolved and charted their unique course in the blockchain evolution timeline.
Blockchain Technology Timeline
As illustrated in the Blockchain Technology Timeline above, Blockchain’s trajectory is a robust response to all skeptics who questioned its value, dismissing it as a fleeting trend.
The journey of Blockchain, from where it began to where it is now headed, testifies to the speed and breadth with which the advantages of this revolutionary technology have been recognized and incorporated into numerous procedures across a multitude of industries. We delve into these in our specially curated handbook for entrepreneurs, the “Entrepreneur’s Guide to Blockchain”.
The potential benefits tied to the applications of Blockchain technology have not gone unnoticed by industry frontrunners. Discussions that once revolved around Bitcoins and Cryptocurrencies have now been channeled toward Blockchain technology.
Blockchain technology, accompanied by its advantageous features, is now at the heart of the growth narratives of many successful industries. This has spurred the demand for Blockchain App Development Agencies that can assist businesses in harnessing this transformative technology for their prosperity. Numerous real-world applications of blockchain technology demonstrate its potential to revolutionize the world, even without cryptocurrency’s involvement.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain operates as a shared, distributed ledger with decentralized control, comprising blocks interconnected into chains. Each chain encrypts data partially using information from the previous block to secure the encryption. Blockchain ledgers can be either public or private; some allow open participation, while others necessitate invitation and access rights. Key advantages of blockchain technology include encryption, provenance, and immutability.
Encryption scrambles data, making it incomprehensible without an associated key. Provenance represents a trail of data, confirming the validity and authenticity of its history. Immutability ensures that once validated, a block’s data cannot be altered. The integration of decentralization with encryption, provenance, and immutability results in a novel, disruptive, secure technology, primed to transform industries globally.
The encrypted data contained in each block of a blockchain can vary based on the system designers’ requirements. In the banking sector, a block may include a name, account number, transaction type, amount, or other pertinent details. In retail scenarios, the blockchain data could include the purchased item, its serial number, purchase date, and manufacturing location.
Companies considering blockchain adoption pinpoint transaction-specific information and incorporate that data into the blocks that make up the blockchain according to their needs. There are virtually no limits to the industries or types of transactions that can benefit from blockchain technology. A growing number of companies across diverse markets already have operational implementations as blockchain continues to present an increasing variety of use cases globally.
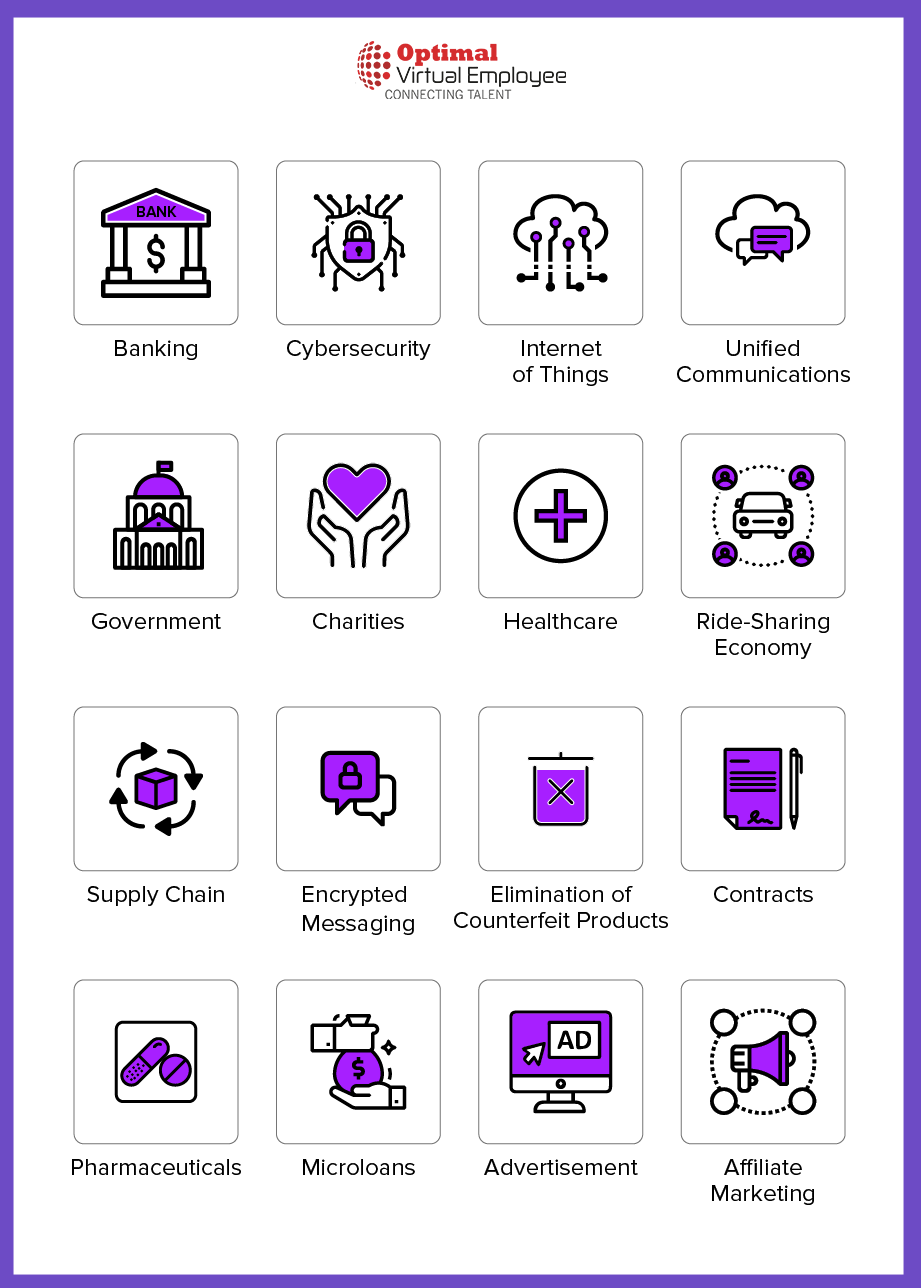
Here are some of the most notable applications of Blockchain that have been identified across various industries:
Banking
In the realm of Banking, there is a plethora of applications for Blockchain technology that extends beyond digital currency exchange.
Some of the notable ones, which to varying degrees involve blockchain and cryptocurrencies, include:
Fraud Reduction – The implementation of a distributed ledger containing timestamped information, with batches of specific transactions linked to another block, makes Blockchain a potent tool for mitigating fraud in banking. This system would make it virtually impossible for hackers to penetrate without the timestamp of the breach becoming conspicuously highlighted.
KYC – Banks are estimated to expend between $60 million to $500 million annually on ‘Know Your Customer’ initiatives. These efforts aim to mitigate money laundering and exclude terrorists from the banking ecosystem. If the KYC process is transitioned to Blockchain, the verification time and associated costs would be significantly reduced.
Blockchain in Cybersecurity
In typical business scenarios involving cloud and computer network usage, data is generally stored on centralized servers. Storing all your business data on a centralized system exposes it to risks such as corruption, data loss, human error, and hacking.
However, by adopting a distributed, decentralized system through the Blockchain-as-a-Service model, the likelihood of cyber attacks can be dramatically reduced
Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Envision purchasing some apples from an online store. When your delivery arrives, you discover that the majority of the apples are already spoiled. Assuming the store doesn’t offer refunds, you’re left in a bind, aren’t you?
But what if there was a preventive measure for such scenarios?
Blockchain technology provides a solution to these issues, enabling traceability throughout the entire supply chain. It can be used to track all sorts of transactions in a secure and transparent fashion.
In supply chain management, blockchain provides permanent record-keeping, transparency, and validation of transactions shared by multiple supply chain partners. With this, anyone can verify the authenticity or status of the product being delivered.
Walmart is developing a blockchain-based distributed ledger to establish connections and monitor the movement of pork suppliers, shippers, buyers, and other parties involved in its distribution across China. In this context, blockchain minimizes the likelihood of data manipulation or discrepancies.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) intertwines various interconnected devices, linking different aspects of a user’s life together. However, this interconnectedness also exposes vulnerabilities. Once one device is compromised, it opens the door for potential attacks on all connected devices, magnifying the risk.
By integrating Blockchain technology with IoT, data exchange occurs directly on the platform rather than relying on third-party intermediaries. This enhances security and privacy. Moreover, the addressable nature of Blockchain-equipped devices allows businesses to access valuable usage histories, aiding in troubleshooting processes.
Unified Communications
Blockchain revolutionizes automated communications, making them safer, faster, and more reliable. While automation is already widespread across various industries, these interactions are typically asynchronous. Blockchain introduces a paradigm shift by facilitating more bi-directional and authorized communications.
In the era of chatbots, Blockchain becomes a vital business solution, especially when bots interact with one another. It addresses challenges related to transparency and time-stamping, ensuring a seamless and trustworthy communication environment.
Blockchain in Voting
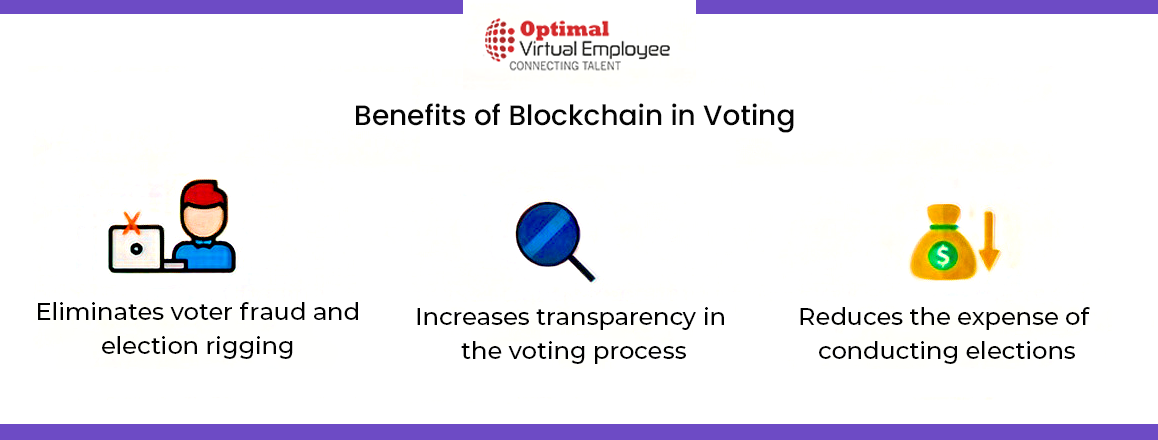
Let’s explore the current voting system. Initially, a voter provides their voter ID, which is subsequently verified. Then, they place their vote via a centralized Electronic Voting Machine (EVM). Yet, this system can be prone to hacking and vote manipulation due to its centralized nature. Fortunately, a decentralized blockchain-based system could potentially eradicate these flaws and uphold the integrity of the elections.
Let’s envisage a blockchain-empowered voting process.
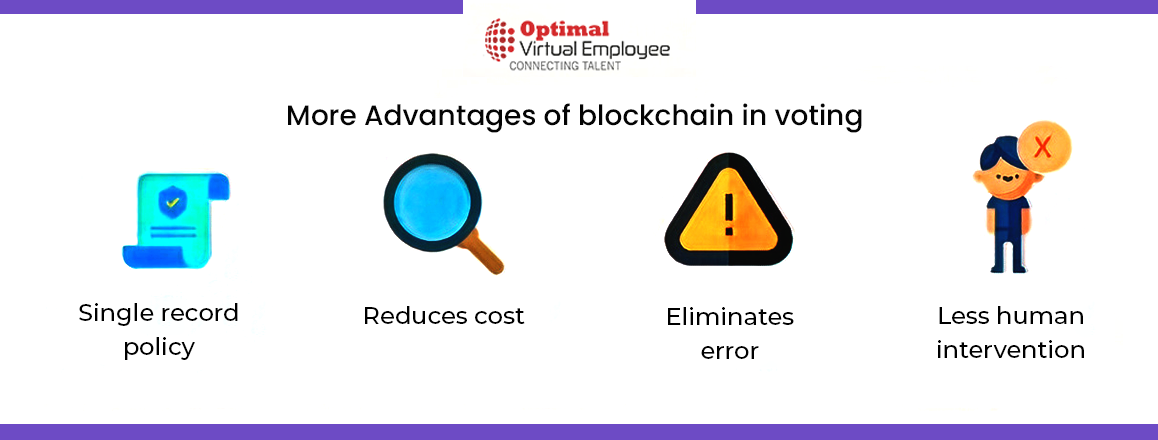
To begin with, a voter would download a voting application, such as MiVote. They would then input their voter ID to register for the election. Once the user’s identity is authenticated, they are permitted to vote, with the advantage of maintaining their anonymity in public. The vote is irrevocably recorded on the blockchain, ensuring its permanence. This guarantees absolute accuracy in vote counting, as each ID corresponds to a single vote. Furthermore, blockchain technology allows voters to track their votes.
Despite still being under development, the integration of blockchain into voting systems could potentially provide unparalleled transparency by eliminating the need for third-party systems.
MiVote is a blockchain platform leveraging tokenization, akin to a digital ballot box. It safeguards both the validity of the voting process and the overall election security.
There are other sectors where blockchain finds its applications:
Insurance: By employing blockchain technology, insurance companies can deter fraudulent activities and prevent false claims.
Real Estate: The introduction of blockchain in real estate can accelerate the conveyance process and remove the need for cash transactions.
Healthcare: Blockchain is being praised for its potential to maintain crucial patient data securely and safely due to its immutable, decentralized nature and transparency.
Government
Blockchain has become a buzzword in governmental and political circles. Numerous government use cases for blockchain have emerged that enhance service quality, protect citizens’ property rights, streamline bureaucratic processes, and augment transparency.
While countries around the world, including Dubai, China, and the US, are examining blockchain’s potential to enhance their societies, Ethereum remains the most commonly adopted platform.
Here are some instances of how various governments are utilizing the Ethereum blockchain to better their nations:
– Dubai has set ambitious plans to evolve into a fully integrated blockchain-based city by 2020.
– Estonia has transitioned into a ‘digital republic’ by moving several of its national systems onto the Ethereum blockchain.
– Chile utilizes Ethereum to monitor financial and data flows within its energy grid. The goal is to curb exploitation and corruption by making the data accessible to its citizens.
– Canada is piloting the platform to provide transparency in government grant usage, in response to citizens’ concerns about corruption and misappropriation.
Charities
A primary concern that deters people from donating is uncertainty about whether their contributions are being used as intended. By implementing blockchain technology, assurances can be made that funds are utilized exactly as planned.
To instill transparency in the system, numerous Bitcoin-based charities are emerging. These organizations provide donors with the ability to see exactly how their contributions are being utilized.
Healthcare
The increasing number of blockchain applications in healthcare is a testament to the transformative power of this technology. Blockchain’s immutable architecture allows Electronic Health Records (EHR) to be stored in a way that is highly resistant to breaches or hacks. Also, blockchain is being employed by developers in developing personalized treatment plans and new medicines.
Ride-Sharing Economy
When applied to ride-sharing, blockchain has the potential to disrupt industry giants like Uber. This technology can address issues such as the company deducting a portion of the driver’s earnings or imposing one-sided terms and conditions. Blockchain, as utilized by Arcade City, returns control to riders and drivers, enabling them to make decisions without reliance on a controlling entity.
Encrypted Messaging
Blockchain enhances end-to-end encryption through decentralization. Companies like Crypviser are leading the way in creating blockchain-based communication platforms. Such platforms provide a secure environment for sending encrypted messages with minimal risk of being hacked, making them particularly valuable within enterprise systems.
Counterfeit Products Elimination
Blockchain’s immutability simplifies tracing the chain of asset ownership for businesses. Storing serial numbers on a blockchain allows parties to verify a product’s authenticity. For instance, De Beers, the world’s largest diamond producer, utilizes blockchain to keep a record of registered diamonds and reduce conflict diamond transactions.
Contracts
Smart contracts, self-executing programs enabled by blockchain, eliminate the need for intermediaries by verifying and processing transactions based on contract rules. Smart contracts find numerous applications across various industries that rely on contract creation in their processes.
Pharmaceuticals
With the World Health Organization estimating that one in ten medical products in low and medium-income countries are sub-standard or falsified, blockchain can play a crucial role. Verifier, a smartphone app, uses a phone’s camera to conduct a spectral analysis on drugs and uploads it to a blockchain for verification, combating pharma fraud.
Microloans
Blockchain’s decentralized ledger has revolutionized the microloan approval process by making it real-time and secure. For example, Twigga, a B2B logistics platform for food stalls in Africa, uses blockchain to manage the entire lending process, from loan application to repayment conditions.
Advertisement
Blockchain can be a game-changer for advertisers, as it can connect various service providers and ensure accurate targeting. Additionally, it protects advertisers from fraudulent web traffic by tracking visitor origins and verifying authenticity.
Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing, where businesses pay a commission to social media promoters, is based on trust. Blockchain and smart contracts ensure funds are transferred to promoters only upon completion of specific tasks, thereby increasing reliability and transparency in affiliate marketing.
Blockchain in Customer Loyalty Programs
Firms like Gyft and Loyal have been leveraging blockchain technology to reward customers with tokens instead of traditional gift cards. This method not only reduces card wastage and potential fraud but also bypasses the need for intermediaries in handling financial transactions.
Blockchain in the Music Industry
Blockchain technology offers promising solutions for content creation, sharing, licensing, distribution, digital usage, payments, and royalties in the music industry. Imogen Heap’s blockchain project, Mycelia, empowers musicians by giving them more control over their work and its distribution. JAAK also initiated a blockchain pilot program aiming to tackle royalty payment issues. While there is ongoing debate regarding the technology’s suitability, many believe that as an understanding of blockchain grows, its benefits to the music industry will become more apparent.
Blockchain in Arms Tracking
Blockchain can be an effective tool in inhibiting illegal arms sales in the black market. A global, unalterable database can record every stage of a weapon’s journey, from manufacturing to final purchase. Such a database would transparently document each transaction and purchase.
Additional applications of blockchain encompass:
Insurance: Blockchain assists insurance companies in preventing fraud and deterring false claims.
Real Estate: The application of blockchain in real estate can expedite the conveyance process and eliminate the need for cash transactions.
Healthcare: The incorruptibility, decentralization, and transparency of blockchain make it a promising tool for preserving vital patient data securely.
Blockchain and the Future
Evidently, the scope of blockchain technology extends far beyond the realm of cryptocurrencies. It’s potential to safeguard democratic processes, provide more secure financial transactions, and revolutionize supply chain management can be instrumental in elevating your career.
Looking at these practical applications of blockchain, it’s clear how this technology can efficiently decentralize various economies. Consequently, numerous global leading brands, in collaboration with top-tier blockchain app development companies, have begun to explore this technology, aspiring to parallel their business growth trajectory with the expansion in future uses of blockchain. You may also wish to consider.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while blockchain technology is most notably recognized for its role in underpinning cryptocurrencies, its potential applications extend far beyond this realm. The unique characteristics of blockchain, such as its immutability, decentralization, and transparency, make it a powerful tool for a diverse range of sectors.
Industries ranging from healthcare, real estate, and insurance to music, advertising, and even weapons tracking are beginning to understand and harness the power of blockchain. It’s being used to streamline processes, increase security, enhance transparency, and reduce the reliance on intermediaries.
From revolutionizing loyalty reward programs to preventing the sale of illegal arms on the black market, blockchain technology has shown immense promise. Its ability to safeguard electronic health records, ensure the authenticity of products, and facilitate secure financial transactions, among other applications, suggests a future where blockchain will play a pivotal role in reshaping numerous aspects of our daily lives.
Therefore, the use of blockchain goes significantly beyond cryptocurrency. Its vast array of potential applications highlights its potential to disrupt traditional systems and processes, ushering in a new era of transparency, efficiency, and security. As we continue to explore and understand this technology better, its transformative potential will likely become even more apparent.